Comparing Notch and Impact Tests with Charpy Impact Tester

Vishal Malhotra-Testing Instrument Expert
22-05-2025
When we build things like bridges, cars, or even plastic toys, we need to make sure the materials are strong and won’t break easily. Two important tests, the Charpy impact test and the Izod impact test, help us check how tough materials are when hit hard. These tests use machines called the Charpy Impact Tester and Izod impact tester, and they often involve a small cut, or “notch,” in the material to see how it handles stress. In this blog, we’ll explain the notch test vs impact test, go over the notch test procedure and notch test formula, describe the Charpy V-notch test procedure, and look at Charpy V-notch test results. We’ll also compare the Charpy impact test and Izod impact test in a way that’s easy to understand.
Principles of Impact Testing
Impact testing assesses a material’s capacity to absorb energy under high velocity loading, replicating scenarios such as mechanical impacts or collisions. The Charpy impact test and Izod impact test utilize pendulum driven systems to deliver a controlled strike to a notched specimen, measuring the energy dissipated during fracture. The notch, a machined stress concentrator, amplifies susceptibility to brittle failure, enabling precise evaluation of toughness.
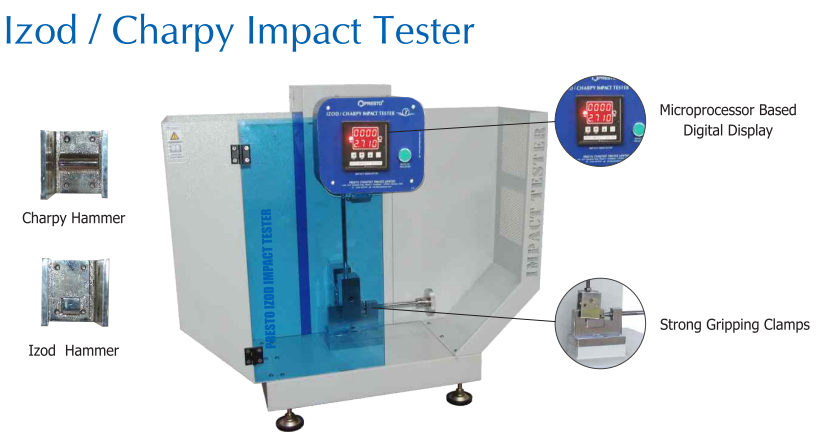

Charpy Impact Test Methodology
The Charpy impact test, conducted with a Charpy Impact Tester | Charpy Impact Tester, is a standardized protocol (ASTM E23, ISO 148) that quantifies the energy required to fracture a notched specimen. The Charpy V-notch test, a prevalent variant, employs a rectangular specimen with a precisely machined V-notch to induce stress concentration.
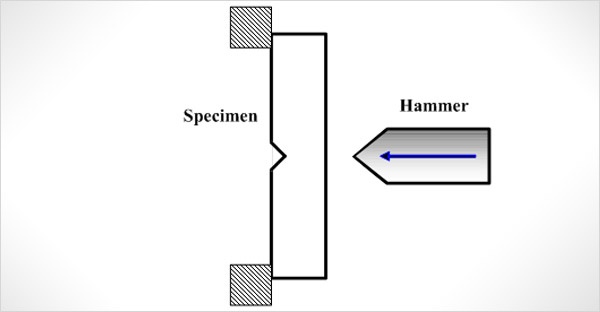
The Charpy V-notch test procedure comprises:
- Specimen Fabrication: A specimen (10 mm × 10 mm × 55 mm) is machined with a 2 mm deep V-notch, featuring a 45° angle and 0.25 mm root radius, per ASTM specifications.
- Specimen Mounting: The specimen is positioned horizontally across two anvils in the Charpy Impact Tester, with the notch oriented opposite the pendulum’s impact trajectory.
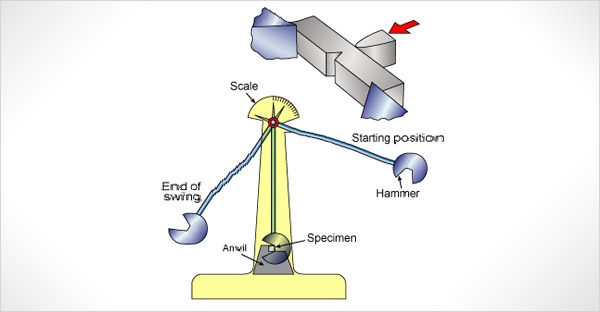
- Impact Execution: A pendulum, released from a calibrated height, strikes the specimen, inducing fracture.
- Energy Measurement: The energy absorbed is derived from the differential between the pendulum’s initial and final swing heights.
- Data Analysis: Charpy V-notch test results are expressed in joules, quantifying toughness. Temperature-dependent tests may also determine the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature.
Charpy V-notch test results are pivotal for materials in critical applications, such as pressure vessels, pipelines, and structural steel, where low-temperature brittleness poses a risk. The energy absorbed reflects the material’s resistance to catastrophic failure under impact.
Izod Impact Test Methodology
The Izod impact test, performed using an Izod impact tester, evaluates toughness under similar principles but with distinct specimen configuration. Standardized under ASTM D256 or ISO 180, it is frequently applied to polymers, composites, and select metals.
The Izod impact test procedure entails:
- Specimen Preparation:- A specimen (10 mm × 10 mm × 75 mm) is machined with a V-notch analogous to the Charpy configuration.
- Specimen Clamping:- The specimen is fixed vertically in the Izod impact tester, with the notch facing the pendulum’s impact path.
- Impact Application:- The pendulum strikes the notched face, causing fracture.
- Energy Quantification: The absorbed energy is recorded in joules or foot-pounds.
The Izod impact test is optimized for materials exhibiting complex fracture behavior, such as thermoplastics and fiber-reinforced composites, providing data on impact resistance in applications like automotive components.
Notch Test vs. Impact Test: Conceptual Differentiation
The notch test evaluates material response to localized stress concentrations, simulating defects such as cracks or surface imperfections. In contrast, an impact test quantifies energy absorption under dynamic loading. The Charpy impact test and Izod impact test integrate a notch test by employing notched specimens, but their primary metric is impact energy, distinguishing them from standalone notch tests focused on stress intensity.
Notch Test Procedure
The notch test procedure is integral to specimen preparation:
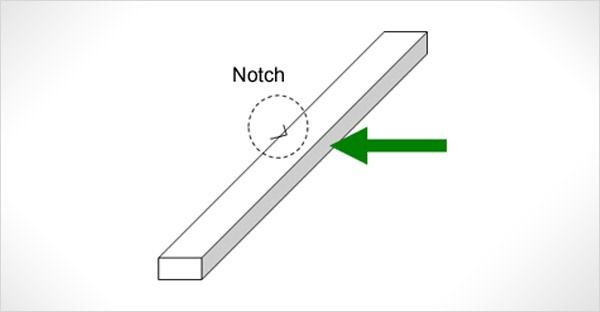
- Notch Machining – A V-notch or U-notch is machined using precision tools (e.g., broaching or milling), adhering to standards (e.g., 2 mm depth, 45° angle for V-notch).
- Geometric Verification – Notch dimensions are measured to ensure compliance with ASTM or ISO tolerances.
- Mechanical Testing – The notched specimen is subjected to impact loading to assess fracture characteristics.
- Result Interpretation – Data elucidate the material’s notch sensitivity, informing design against brittle failure.

Notch Test Formula
The notch test formula for impact tests calculates the energy absorbed during fracture:
E = m × g × (h1 - h2)
Where:
- E = energy absorbed (joules)
- m = pendulum mass (kg)
- g = gravitational acceleration (9.81 m/s2)
- h1 = initial pendulum height (m)
- h2 = final pendulum height (m)
This metric quantifies the material’s toughness, with lower values indicating heightened notch sensitivity.
Comparative Analysis: Charpy vs. Izod Impact Tests
The Charpy impact test and Izod impact test diverge in specimen configuration, application, and standardization. The table below delineates these distinctions:
| Parameter | Charpy Impact Test | Izod Impact Test |
| Specimen Orientation | Horizontal, supported on anvils | Vertical, clamped at base |
| Notch Orientation | Opposite pendulum impact | Aligned with pendulum impact |
| Apparatus | Charpy Impact Tester | Izod Impact Tester |
| Material Focus | Metals (e.g., steel, aluminum) | Polymers, composites, select metals |
| Standards | ASTM E23, ISO 148 | ASTM D256, ISO 180 |
| Energy Units | Joules or foot-pounds | oules or foot-pounds |
The Charpy impact test is predominant in metallurgical applications, particularly for low-temperature assessments, while the Izod impact test is suited for non-metallic materials requiring vertical specimen constraint.
Engineering Applications
The Charpy V-notch test is indispensable in industries such as oil and gas, where pipeline integrity at subzero temperatures is critical, and aerospace, where component reliability under impact is non-negotiable. The Izod impact test informs the design of plastic components in automotive, medical, and consumer electronics, ensuring durability against dynamic stresses.
Impact Testing Essentials: Charpy and Izod FAQs
Q1. What differentiates the Charpy impact test from the Izod impact test?
Ans. The Charpy impact test employs a horizontal specimen with the notch opposite the impact, suited for metals, whereas the Izod impact test uses a vertical specimen with the notch facing the impact, optimized for polymers.
Q2. Why is a V-notch utilized in the Charpy V-notch test?
Ans. The V-notch induces a stress concentration, replicating defects and enabling the Charpy V-notch test to quantify susceptibility to brittle fracture under impact.
Q3. How are Charpy V-notch test results applied in material selection?
Ans. Charpy V-notch test results, reported in joules, indicate toughness. Higher values denote enhanced resistance to fracture, guiding material selection for high-stakes applications like structural steel.
Q4. Are the Charpy Impact Tester and Izod impact tester interchangeable?
Ans. No, the Charpy Impact Tester and Izod impact tester are designed for distinct specimen configurations and standards, rendering them non-interchangeable for precise testing.
Conclusive Insights on Charpy vs. Izod Testing
The Charpy impact test and Izod impact test, executed via the Charpy Impact Tester and Izod impact tester, are rigorous methodologies for quantifying material toughness. By incorporating a notch test, these protocols assess fracture behavior under stress concentrations, leveraging the notch test procedure and notch test formula. The Charpy V-notch test procedure and its results are critical for metallic applications, while the Izod impact test excels with non-metallics. Discerning notch test vs impact test distinctions enables engineers to select appropriate testing regimes, ensuring material reliability in demanding environments.
Get the Best Impact Tester Price Today!
Looking for a reliable and accurate impact testing solution? Discover industry-leading quality at competitive Impact Tester Price only at Presto.
Call now: +91 9210 903 903
Email: info@prestogroup.com
Don’t compromise on testing precision—get a quote today!
Recent News
- Paper & Packaging Testing Instruments
- Paint, Plating & Coating Testing Instruments
- Plastic & Polymer Testing Instruments
- Environmental Testing Chambers
- PET & Preform Testing Instruments
- Color Measuring Testing Instruments
- View Entire Range Instruments

Catalogue 2023
Get information about new product launches, research, innovation and endeavors at Presto.
download Free CopyNeed more information
Connect with us for your business enquiries. Generally we respond within one or two working days.
send enquiriesContact Us
Get a Quote
